| Vympel R-73 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | short-range air-to-air missile |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1982-present |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Vympel |
| Specifications | |
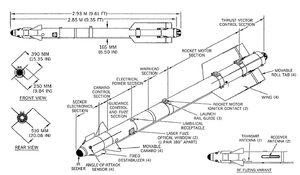
| Mass | 105 kilograms (231 lb) |
| Length | 2.93 metres (9 ft 7 in) |
| Diameter | 165 millimetres (6.5 in) |
| Warhead | 7.4 kilograms (16 lb) |
|
| |
| Engine | solid-fuel rocket engine |
| Wingspan | 510 millimetres (20 in) |
Operational range |
R-73E: 20 kilometres (12 mi) |
| Maximum speed | Mach 2.5 |
Guidance system | All-aspect infrared homing |
Launch platform | |
The Vympel R-73 (NATO reporting name AA-11 Archer) is a short-range air-to-air missile developed by Vympel NPO, that entered service in 1982.
Development[]
The R-73 was developed to replace the earlier R-60 (AA-8 'Aphid') weapon for short-range use by Soviet fighter aircraft. Work began in 1973, and the first missiles entered service in 1982.
The R-73 is an infrared-guided (heat-seeking) missile with a sensitive, cryogenic cooled seeker with a substantial "off-boresight" capability: the seeker can "see" targets up to 40° off the missile's centerline.[3] It can be targeted by a helmet-mounted sight (HMS) allowing pilots to designate targets by looking at them. Minimum engagement range is about 300 meters, with maximum aerodynamic range of nearly 30 km (19 mi) at altitude.
The R-73 is a highly maneuverable missile and mock dogfights have indicated that the high degree of "off-boresight" capability of the R-73 would make a significant difference in combat. The missile also has a mechanically simple but effective system for thrust-vectoring. Altogether this prompted the development of the Sidewinder and other SRM successors like AIM-132 ASRAAM, IRIS-T, MICA IR, Python IV and the latest Sidewinder variant, AIM-9X, that entered squadron service in 2003.
From 1994 the R-73 has been upgraded in production to the R-73M standard, which entered CIS service in 1997. The R-73M has greater range and a wider seeker angle (to 60° off-boresight), as well as improved IRCCM (Infra-Red Counter-Counter-Measures).
An improved version of the R-73M, the R-74M features fully digital and re-programmable systems, and is intended for use on the MiG-35 or MiG-29K/M/M2 and Su-27SM, Su-30MK and Su-35BM.
The weapon is used by the MiG-29, MiG-31, Su-27, Su-34 and Su-35, and can be carried by newer versions of the MiG-21, MiG-23, Sukhoi Su-24, and Su-25 aircraft.[4] India is looking to use the missile on their HAL Tejas. It can also be carried by Russian attack helicopters, including the Mil Mi-24, Mil Mi-28, and Kamov Ka-50.
Operational history[]
On 24 February 1996, two Cessna 337 of the Brothers to the Rescue were shot down by a Cuban Air Force MiG-29UB. Each of the aircraft was downed by a R-73 missile.[5]
During Eritrean-Ethiopian War from May 1998 to June 2000, R-73 missiles were used in combat by both Ethiopian Su-27s and Eritrean MiG-29s. It was the IR-homing R-60 and the R-73 that were used in all but two of the kills. It is reported that R-73 launches were successful less than 10% of the time when fired from both Su-27 and Mig-29.[citation needed]
On March 18, 2008, a MIG-29 Fulcrum of the Russian Air Force intercepted a Georgian Elbit Hermes 450 UAV over Abkhazia. The MIG-29's pilot launched a single R-73 missile at the UAV. The missile struck the UAV and destroyed it.
Operators[]
 Algeria[6]
Algeria[6] Bangladesh[7]
Bangladesh[7] Bulgaria
Bulgaria China
China Cuba
Cuba Eritrea
Eritrea Ethiopia
Ethiopia Georgia Used on SU-25KM Scorpion [8]
Georgia Used on SU-25KM Scorpion [8] India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Iran
Iran Malaysia
Malaysia North Korea
North Korea Peru
Peru Poland
PolandRussia
 Serbia
Serbia Slovakia
Slovakia Ukraine
Ukraine Venezuela
Venezuela Vietnam
Vietnam Egypt
Egypt
Former operators[]
Gallery[]
Notes[]
- ↑ http://www.fas.org/man/dod-101/sys/missile/row/aa-11.htm
- ↑ http://warfare.be/?catid=262&linkid=1673
- ↑ http://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/vympel-reveals-previously-classified-air-to-air-missiles-21026
- ↑ http://www.uuaz.ru/production/su25ub/su25ub_wpn_e.html
- ↑ http://www1.umn.edu/humanrts/cases/86-99.html
- ↑ http://weaponsystems.net/weapon.php?weapon=HH07%20-%20R-73
- ↑ http://www.bdmilitary.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=87&Itemid=111
- ↑ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZAszf4XPTFo
References[]
- Gordon, Yefim (2004). Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War Two. Hinckley, England: Midland Publishing. ISBN 1-85780-188-1.
- http://www.airforce-technology.com/projects/yak_130/ 04. August 2013.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vympel R-73. |
The original article can be found at R-73 (missile) and the edit history here.

