
Europe, 1923.
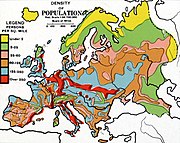
Population densities in Europe, 1923.
The terms interwar period[1][2][3] or interbellum (Latin: inter-, "between" + bellum, "war") nearly always refer to the period between the end of World War I and the beginning of World War II—the period beginning with the Armistice with Germany that concluded World War I in 1918 and the following Paris Peace Conference in 1919, and ending in 1939 with the Invasion of Poland and the start of World War II.
Description of the Interbellum[]
This period of history was marked by turmoil as Europe struggled to recover from the devastation of the First World War and destabilizing effects of the loss of a number of monarchies. Later a period of considerable prosperity (the Roaring Twenties) followed, but this changed dramatically with the onset of the Great Depression in 1929. It was during this time that the Weimar Republic in Germany gave way to two episodes of political and economic turmoil, the first culminated in the German hyperinflation of 1923 and the failed Beer Hall Putsch of that same year. The second convulsion, brought on by the worldwide depression, resulted in the rise of Nazism. In Asia, Japan became an ever more assertive power, especially with regard to China.
One main institution intended to bring stability was the League of Nations, created after the First World War with the intention of maintaining world security and peace and encouraging economic growth between member countries. The League was undermined from the start by the non-participation of the United States and the Soviet Union, and subsequently by the bellicosity of Mussolini's Italy, Nazi Germany, and Imperial Japan - leading many to question its legitimacy and effectiveness.
A series of international crises strained the League to its limits, the earliest being the invasion of Manchuria by Japan and the Abyssinian Crisis of 1935/36, in which Italy invaded Abyssinia, one of the few free African nations at that time. The League tried to enforce economic sanctions upon Italy, but to no avail. The incident highlighted French and British weakness, exemplified by their reluctance to alienate Italy and lose her as their ally. The limited actions taken by the Western powers pushed Mussolini's Italy towards alliance with Hitler's Germany anyway. The Abyssinian war showed Hitler how weak the League was and encouraged his participation in the Spanish Civil War. He also remilitarized the Rhineland in flagrant disregard of the Treaty of Versailles. This was the first in a series of provocative acts culminating in the invasion of Poland in September 1939 and the beginning of the Second World War.

See also[]
- Aftermath of World War I
- Causes of World War II
- European Civil War
- Events preceding World War II in Europe
- List of treaties
References[]
- ↑ Williamson R. Murray, Allan R. Millett. "Military Innovation in the Interwar Period"
- ↑ United States Foreign Policy in the Benjamin D. Rhodes. "Interwar Period, 1918-1941: The Golden Age of American Diplomatic and Military Complacency"
- ↑ Peter M. R. Stirk. "European unity in context: the interwar period"
Bibliography[]
The original article can be found at Interwar period and the edit history here.