| Eastern Rumelia Източна Румелия Iztochna Rumeliya روم الى شرقى Rumeli-i Şarkî | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomous Province of the Ottoman Empire | |||||||||
| 1878–1908a | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Capital | Plovdiv | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1884 census | 975,030 | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| • Type | Autonomous Province | ||||||||
| Governor-General | |||||||||
• 1879–1884 | Alexander Bogoridi | ||||||||
• 1884–1885 | Gavril Krastevich | ||||||||
• 1886 | Alexander of Bulgaria | ||||||||
• 1887–1908 | Ferdinand I of Bulgaria | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 13 July 1878 | |||||||||
• Unification with Bulgaria | 6 September 1885 1908a | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of |
| ||||||||
Eastern Rumelia (Bulgarian language: Източна Румелия , Iztochna Rumeliya; Ottoman Turkish language: روم الى شرقى, Rumeli-i Şarkî; Greek: Ανατολική Ρωμυλία, Anatoliki Romylia) was an autonomous unit (Oblast in Bulgarian, vilayet in Turkish) in the Ottoman Empire, created in 1878 by the Treaty of Berlin and de facto ended in 1885, when it was united with Bulgaria, of which it is a part today. However, it continued to be de jure an Ottoman province until 1908, when Bulgaria declared independence.
Ethnic Bulgarians had an absolute majority within Eastern Rumelia, with a significant ethnic Turk and Greek population. Its capital was Plovdiv (Ottoman: Filibe, Greek: Philippopolis).
History[]
Eastern Rumelia was created as an autonomous province within the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of Berlin in 1878. It encompassed the territory between the Balkan Mountains, the Rhodope Mountains and Strandzha, a region known to all its inhabitants—Bulgarians, Ottoman Turks, Roma, Greeks, Armenians and Jews—as Northern Thrace. The artificial [1] name, Eastern Rumelia, was given to the province on the insistence of the British delegates to the Congress of Berlin: the Ottoman notion of Rumelia refers to all European regions of the empire, i.e. those that were in Antiquity under the Roman Empire. Some twenty Pomak (Bulgarian Muslim) villages in the Rhodope Mountains refused to recognize Eastern Rumelian authority and formed the so-called Republic of Tamrash.
The province is remembered today by philatelists for having issued postage stamps from 1880 on. See the main article, Postage stamps and postal history of Eastern Rumelia.
Unification with Bulgaria[]
After a bloodless revolution on 6 September 1885, the province was annexed by the Principality of Bulgaria, which was de jure a tributary state but de facto functioned as independent nation. After the Bulgarian victory in the subsequent Serbo-Bulgarian War, the status quo was recognized by the Porte with the Tophane Agreement on 24 March 1886. With the Tophane Act, Sultan Abdul Hamid II appointed the Prince of Bulgaria (without mentioning the name of the incumbent prince Alexander of Bulgaria) as Governor-General of Eastern Rumelia, thus retaining the formal distinction between the Principality of Bulgaria and Eastern Rumelia[2] and preserving the letter of the Berlin Treaty.[3] However, it was clear to the Great Powers that the union between the Principality of Bulgaria and Eastern Rumelia was permanent, and not to be dissolved.[4] The Republic of Tamrash and the region of Kardzhali were reincorporated in the Ottoman Empire. The province was nominally under Ottoman suzerainty until Bulgaria became de jure independent in 1908. 6 September, Unification Day, is a national holiday in Bulgaria.
Government[]
According to the Treaty of Berlin, Eastern Rumelia was to remain under the political and military jurisdiction of the Ottoman Empire with significant administrative autonomy (Article 13). The law frame of Eastern Rumelia was defined with the Organic Statute which was adopted on 14 April 1879 and was in force until the Unification with Bulgaria in 1885.[5] According to the Organic Statute the head of the province was a Christian Governor-General appointed by the Sublime Porte with the approval of the Great Powers. The legislative organ was a Provincial Counsel which consisted of 56 persons, of which 10 were appointed by the Governor-General, 10 were permanent and 36 were directly elected by the people.
The first Governor-General was the Bulgarian prince Alexander Bogoridi (1879–1884) who was acceptable to both Bulgarians and Greeks in the province. The second Governor-General was Gavril Krastevich (1884–1885), a famous Bulgarian historian. Before the first Governor-General, Arkady Stolypin was the Russian Civil Administrator from 9 October 1878 to 18 May 1879.
During the period of Bulgarian annexation Georgi Stranski was appointed as a Commissioner for South Bulgaria (9 September 1885 - 5 April 1886), and when the province was restored to nominal Ottoman sovereignty, but still under Bulgarian control, the Prince of Bulgaria was recognized by the Sublime Porte as the Governor-General.
- Alexander Bogoridi (Aleko Pasha; 18 May 1879 - 26 April 1884)
- Gavril Krastevich (Gavril Pasha; 26 April 1884 - 18 September 1885)
- Alexander of Bulgaria (17 April 1886 - 7 September 1886)
- Ferdinand I of Bulgaria (7 July 1887 - 5 October 1908)
Administrative divisions[]

Map of the administrative divisions of Eastern Rumelia
Eastern Rumelia consisted of the departments (called in Bulgarian окръзи okrazi, in Ottoman terminology sanjaks ) of Plovdiv (Filibe), Pazardzhik (Tatarpazarcığı), Haskovo (Hasköy), Stara Zagora (Eski Zağra), Sliven (İslimye) and Burgas (Burgaz), in turn divided into 28 cantons (equivalent to Bulgarian околии okolii, Ottoman kazas).[6]
The cantons were:
- Department of Plovdiv: Plovdiv, Konush (the canton seat was in Stanimaka), Ovchi Halm (seat in Golyamo Konare), Stryama (seat in Karlovo), Sarnena Gora (seat in Brezovo) and Rupchos (seat in Chepelare)b
- Department of Pazardzhik: Pazardzhik, Peshtera, Panagyurishte and Ihtiman
- Department of Haskovo: Haskovo, Hadzhi Eles, Harmanli and Kardzhalic
- Department of Stara Zagora: Stara Zagora, Kazanlak, Chirpan, Nova Zagora and Tarnovo Seymen
- Department of Sliven: Sliven, Yambol, Kazalagach, Kavakli and Kotel
- Department of Burgas: Burgas, Anhialo, Karnobat and Aytos
Population and ethnic demographics[]

Ethnic composition map of the Balkans by the German-English cartographer E. G. Ravenstein in 1870.

Ethnic composition map of the Balkans by A. Synvet in 1877, a French professor of the Ottoman Lyceum of Constantinople. It was considered as pro-Greek by later historians.[7]
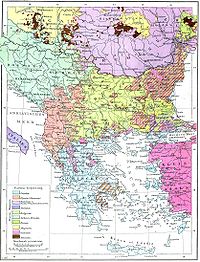
Ethnic composition map of the Balkans from Andrees Allgemeiner Handatlas, 1st Edition, Leipzig 1881.
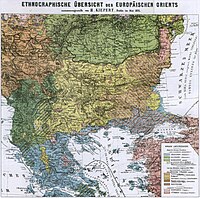
Ethnic composition map of the Balkans by the German Geograph und Kartograph Heinrich Kiepert in 1882.
The earliest information on the ethnic demographics of Eastern Rumelia, before the first census was conducted, comes from ethnographic maps of the Balkans by Western cartographers. There is however little information on the actual population numbers of the different ethnic groups before 1878. According to a British report before the 1877–1878 war, the non-Muslim population (which were mostly Bulgarians) of Eastern Rumelia, was about 60% which proportion grew due to the flight and emigration of Muslims during and after the war.[8]
The results of the first Regional Assembly elections of 17 October 1879 show a predominantly Bulgarian character: Of the 36 elected deputies, 31 were Bulgarians (86.1%), 3 were Greeks (8.3%) and two were Turks (5.6%).[9] The ethnic statistics from the censuses of 1880 and 1884 show a Bulgarian majority in the province. In the discredited[10] census of 1880, out of total population of 815,951 people some 590,000 (72.3%) self-identified as Bulgarians, 158,000 (19.4%) as Turks, 19,500 (2.4%) as Roma, and 48,000 (5.9%) belonged to other ethnicities,[11] notably Greeks, Armenians and Jews. The repetition of the census in 1884 returned similar data: 70.0% Bulgarians, 20.6% Turks, 2.8% Roma and 6.7% others.[12]
The Greek inhabitants of Eastern Rumelia were concentrated on the coast, where they were strong in numbers,[13] and certain cities in the interior such as Plovdiv, where they formed a substantial minority. Most of the Greek population of the region was exchanged with Bulgarians from the Greek provinces of Macedonia and Thrace in the aftermath of the Balkan Wars and World War I. As of 2001, there are about 3400 Greeks in Bulgaria, and about 4100 Sarakatsani.
Eastern Rumelia was also inhabited by foreign nationals, most notably Austrians, Czechs, Hungarians, French people and Italians.
The ethnic composition of the population of Eastern Rumelia, according to the provincial census taken in 1884, was the following:[12]
| Ethnicity (1884 census) | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Bulgarians | 681,734 | 70.0% |
| Turks | 200,489 | 20.6% |
| Greeks | 53,028 | 5.4% |
| Roma (Gypsies) | 27,190 | 2.8% |
| Jews | 6,982 | 0.7% |
| Armenians | 1,865 | 0.2% |
| Total | 975,030 | 100% |
The population's ethnic composition in the Bulgarian provinces of Pazardzhik, Plovdiv, Stara Zagora, Haskovo, Sliven, Yambol and Burgas, which have approximately the same territory as Eastern Rumeliad according to the 2001 census is the following:
| Ethnicity (2001 census)[14] | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Bulgarians | 2,068,787 | 83.7% |
| Turks | 208,530 | 8.4% |
| Roma (Gypsies) | 154,004 | 6.2% |
| Armenians | 5,080 | 0.2% |
| Russians | 4,840 | 0.2% |
| Greeks | 1,398 | 0.1% |
| Jews | 251 | |
| Others | 8,293 | 0.3% |
| Unspecified | 21,540 | 0.9% |
| Total | 2,472,723 | 100% |
Ownership[]

Turkish refugees from Eastern Rumelia 1885 - The Illustrated London News, author: Richard Caton Woodville, Jr.
Property abandoned by Muslims fleeing the Russian army during the 1877–1878 war was appropriated by the local population. The former owners, mostly large landholders, were threatened with trial by military court if they had committed crimes during the war, so that they would not return. Two Turkish landowners who did return were in fact sentenced to death thus preventing others from desiring to come back. Those Turkish landowners who were not able to take possession of their land were financially compensated, with the funds collected by the Bulgarian peasants, some of whom were indebted as a result. For those who did return a 10% property tax was issued, forcing many to sell off their property in order to pay the tax.[15][16] Michael Palairet claimed that land rights of Muslim owners were largely disregarded despite of being guaranteed by the powers and de-Ottomanization of Bulgaria and Eastern Rumelia led to the economic decline in the region,[17] which is contradicted by many other authors, who show rapid growth of the economy as well as rapid industrial development and growth of exports in Bulgaria after 1878.[18][19][20]
Notes and references[]
Notes[]
^a From 1885 Eastern Rumelia was de facto part of the Principality of Bulgaria
^b The western part of this canton refused to recognize the authority of Eastern Rumelia, formed the so-called Republic of Tamrash and in 1886 was ceded back to the Ottoman Empire by the Tophane Agreement
^c The canton of Kardzhali was ceded back to the Ottoman Empire by the Tophane Agreement
^d Burgas, Haskovo, and Pazardzhik provinces also include territory that was not part of Eastern Rumelia, while other parts of Eastern Rumelia are now in the provinces of Sofia, Smolyan and Kardzhali. The de-facto independent Republic of Tamrash, which is now divided between the provinces of Smolyan and Plovdiv, didn't participate in the 1884 census.
References[]
- ↑ Balkan studies: biannual publication of the Institute for Balkan Studies, Volume 19, 1978, p.235
- ↑ Emerson M. S. Niou, Peter C. Ordeshook, Gregory F. Rose. The balance of power: stability in international systems, 1989, p. 279.
- ↑ Stanley Leathes, G. W. (George Walter) Prothero, Sir Adolphus William Ward. The Cambridge Modern History, Volume 2, 1908, p. 408.
- ↑ Charles Jelavich, Barbara Jelavich. The establishment of the Balkan national states, 1804-1920, 2000, p. 167.
- ↑ See Hertslet, Edward (1891). "The Map of Europe by Treaty; which have taken place since the general peace of 1814. With numerous maps and notes". Her Majesty's Stationery Office. pp. 2860–2865. http://archive.org/stream/mapofeuropebytre04hert#page/2860/mode/2up. Retrieved 2012-12-28.
- ↑ "Historical data about administrative-territorial structure of Bulgaria after 1878". National Statistical Institute of the Republic of Bulgaria. http://www.nsi.bg/nrnm/index.php?i=1&ezik=en.
- ↑ Robert Shannan Peckham, Map mania: nationalism and the politics of place in Greece, 1870–1922, Political Geography, 2000, p.4: [1]
- ↑ Studies on Ottoman social and political history: selected articles and essay, Kemal H. Karpat, p.370
- ↑ Делев, "Княжество България и Източна Румелия", История и цивилизация за 11. клас.
- ↑ Council of Europe, Ministers' Deputies, 6.1 European population committee (CDPO), Section 3 https://wcd.coe.int/wcd/ViewDoc.jsp?id=429995&Site=COE
- ↑ "Eтнически състав на населението в България. Методологически постановки при установяване на етническия състав" (in Bulgarian). MIRIS - Minority Rights Information System. http://miris.eurac.edu/mugs2/do/blob.html?type=html&serial=1039432230349. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "6.1 European population committee (CDPO)". Council of Europe. p. II. The Demographic Situation of Ethnic/minority Groups 1. Population Size and Growth. https://wcd.coe.int/ViewDoc.jsp?id=429995&Site=COE.
- ↑ A Short History of Russia and the Balkan States, Donald Mackenzie Wallace, 1914, p.102
- ↑ http://www.nsi.bg/Census/Ethnos.htm
- ↑ Jelavich, p. 164.
- ↑ The Balkans since 1453; Leften Stavros Stavrianos, Traian Stoianovich; p. 442
- ↑ Palairet, Michael R.,"The Balkan Economies C.1800-1914: Evolution Without Development", 1997 [2] pp.174-202
- ↑ An Economic and Social History of the Ottoman Empire, Volume 2; Halil İnalcık, Donald Quataert; 1997; p. 381
- ↑ The Balkans Since 1453; Leften Stavros Stavrianos; 2000; p.425
- ↑ The Industrial Revolution in National Context: Europe and the USA; Mikulas Teich, Roy Porter; 1996; p.300
- Делев, Петър; Валери Кацунов, Пламен Митев, Евгения Калинова, Искра Баева, Боян Добрев (2006) (in Bulgarian). История и цивилизация за 11. клас. Труд, Сирма.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eastern Rumelia. |
The original article can be found at Eastern Rumelia and the edit history here.