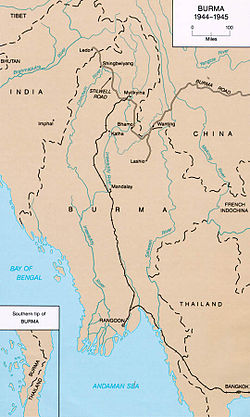
Burma Road and Ledo Road in 1944

The "24 Turns" (25.821725°N, 105.202600°E), often mistaken for a segment of the Burma Road, is actually in Qinglong, Guizhou. During the Second Sino-Japanese War, the war supplies first arrived at Kunming by the Burma Road, then went through the "24 Turns" to arrive at Chongqing, the provisional capital, and reach the front-line troops.

Burmese and Chinese laborers using hand tools to build Burma Road
The Burma Road (Chinese language: 滇缅公路) is a road linking Burma (also called Myanmar) with the southwest of China. Its terminals are Kunming, Yunnan, and Lashio, Burma. When it was built, Burma was a British colony occupied by the Japanese.
History[]
The road is 717 miles (1,154 km) long and runs through rough mountain country.[1] The sections from Kunming to the Burmese border were built by 200,000 Burmese and Chinese laborers during the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937 and completed by 1938.[2] It had a role in World War II, when the British used the Burma Road to transport materiel to China before Japan was at war with the British. Supplies would be landed at Rangoon (now Yangon) and moved by rail to Lashio, where the road started in Burma. In 1940 the British government yielded to Japanese diplomatic pressure to close down the Burma Road to supplies to China for a period of three months. After the Japanese overran Burma in 1942, the Allies were forced to supply Chiang Kai-shek and the nationalist Chinese by air. They flew these supplies from airfields in Assam, India, over "the hump", the eastern end of the Himalaya uplift. At the insistence of the United States, and much to the chagrin of Winston Churchill, the wartime leader of Britain, British forces were given, as their primary goal in the war against Japan, the task of recapturing Burma and reopening land communication with China. Under British command Indian, British, Chinese, and American forces, the latter led by Vinegar Joe Stilwell, defeated a Japanese attempt to capture Assam and recaptured northern Burma. In this area they built a new road, the Ledo Road which ran from Ledo Assam, through Myitkyina and connected to the old Burma Road at Wandingzhen, Yunnan, China. The first trucks reached the Chinese frontier by this route on January 28, 1945. (Winston Churchill, The Second World War, v. VI, chap. 11.)
Films set on the Burma Road[]
- Burma Convoy (1941)
- A Yank on the Burma Road (1942)
- Bombs over Burma (1942)
Further reading[]
- C. T. Chang: Burma Road, Malaysia Publications, Singapore 1964.
- Forbes, Andrew ; Henley, David (2011). China's Ancient Tea Horse Road. Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Books. ASIN: B005DQV7Q2
- Jon Latimer: Burma:The Forgotten War. John Murray, London 2004, ISBN 0-7195-6576-6.
- Donovan Webster: The Burma Road: The Epic Story of the China-Burma-India Theater in World War II. Farrar Straus & Giroux, New York City, NY 2003, ISBN 0-374-11740-3.
See also[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Burma Road. |
- Ledo Road
- Yunnan-Burma Railway
- Salween River Bridge
References[]
- ↑ Burma Road - Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- ↑ Seagrave, Gordon S., Burma Surgeon, W. W. Norton & Company, New York, 1943
External links[]
- Merrill's Marauders: Protecting The Burma Road
- Burma Road photos
- WW2 - Campaigns in Burma World War II Burma Road video
- WWII - Why We Fight - The Battle of China 1943 video 1
- WWII - Why We Fight - The Battle of China 1943 video 2
- Life-line to China Re-Opened, 1945/02/12 (1945) Universal Newsreel
- The Ghost Road Mark Jenkins, magazine, October 2003
- Blood, Sweat and Toil along the Burma Road Donovan Webster, National Geographic Magazine, November 2003
- Burma Road on bicycle Erin O'Brien, The Cultured Traveler, Vol 6 April 2004
- China to Europe via a new Burma road David Fullbrook, Asia Times, September 23, 2004
- On the way to MandalayThe Sydney Morning Herald, August 16, 2008
- Los Angeles Times, "Burma's Stilwell Road: A backbreaking WWII project is revived", December 30, 2008.
- Transcribed copies of Joseph Warren Stilwell's World War II diaries are available on the Hoover Institution Archives website, with the original diaries among the Joseph Warren Stilwell papers at the Hoover Institution Archives.
- Transcribed copies of the World War II diaries of Ernest F. Easterbrook, Stilwell's executive assistant in Burma (as of 1944) and son-in-law, are available on the Hoover Institution Archives website, with the original diaries among the Ernest Fred Easterbrook papers at the Hoover Institution Archives.
The original article can be found at Burma Road and the edit history here.