m (→External links: Remove some templates. interwiki links, delink non military terms, cleanup and move Wikipedia link above categories) |
m (Remove uneeded parameters from Template:Aircraftspecs and cleanup) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {|{{Infobox |
+ | {|{{Infobox aircraft begin |
|name = BV P.213 |
|name = BV P.213 |
||
|image =BV P-213.jpg |
|image =BV P-213.jpg |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
This plane is one of the products of the latter part of 1944, when the High Command of the [[Luftwaffe]] saw that there was a dire need to put up a strong defense against the devastating [[Allied bombing of Germany|allied bombing raids]]. |
This plane is one of the products of the latter part of 1944, when the High Command of the [[Luftwaffe]] saw that there was a dire need to put up a strong defense against the devastating [[Allied bombing of Germany|allied bombing raids]]. |
||
| − | Thus aircraft manufacturers [[Heinkel]], [[Junkers]] and Blohm & Voss were asked by the Luftwaffe in November to come up with light fighter designs using a strict minimum of materials that would be fitted with one [[Argus As 014]] pulse jet engine per unit. |
+ | Thus aircraft manufacturers [[Heinkel]], [[Junkers]] and Blohm & Voss were asked by the Luftwaffe in November to come up with light fighter designs using a strict minimum of materials that would be fitted with one [[Argus As 014]] pulse jet engine per unit. |
| − | |||
The resulting planes were small, spartan creations, with no radio and almost no electrical equipment, but the aim was to produce them cheaply and in large numbers so as to overwhelm the Allied bomber formations that flew daily over Germany's skies. |
The resulting planes were small, spartan creations, with no radio and almost no electrical equipment, but the aim was to produce them cheaply and in large numbers so as to overwhelm the Allied bomber formations that flew daily over Germany's skies. |
||
Heinkel would use a [[He 162]] air frame powered by a pulse jet and Junkers would submit the [[Junkers EF 126|Ju EF 126]] project.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.luft46.com/bv/bvp213.html|title=Blohm & Voss BV P.213 Luft '46 entry |publisher=Luft46.com |date= |accessdate=2013-06-01}}</ref> |
Heinkel would use a [[He 162]] air frame powered by a pulse jet and Junkers would submit the [[Junkers EF 126|Ju EF 126]] project.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.luft46.com/bv/bvp213.html|title=Blohm & Voss BV P.213 Luft '46 entry |publisher=Luft46.com |date= |accessdate=2013-06-01}}</ref> |
||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
==Specifications== |
==Specifications== |
||
{{Aircraft specs |
{{Aircraft specs |
||
| − | |ref= |
+ | |ref= |
| + | |prime units?=met |
||
| − | |prime units?=met<!-- imp or kts first for US aircraft, and UK aircraft pre-metrification, |
||
| − | met(ric) first for all others. You MUST choose a format, or no specifications will show --> |
||
| − | <!-- |
||
| − | General characteristics |
||
| − | --> |
||
| − | |genhide= |
||
|crew=one |
|crew=one |
||
| − | |capacity= |
||
|length m=6.2 |
|length m=6.2 |
||
| − | |length ft= |
||
| − | |length in= |
||
| − | |length note= |
||
|span m=6 |
|span m=6 |
||
| − | |span ft= |
||
| − | |span in= |
||
| − | |span note= |
||
|height m=2.28 |
|height m=2.28 |
||
| − | |height ft= |
||
| − | |height in= |
||
| − | |height note= |
||
|wing area sqm=5 |
|wing area sqm=5 |
||
| − | |wing area sqft= |
||
| − | |wing area note= |
||
| − | |aspect ratio=<!-- sailplanes --> |
||
| − | |airfoil= |
||
| − | |empty weight kg= |
||
| − | |empty weight lb= |
||
| − | |empty weight note= |
||
| − | |gross weight kg= |
||
| − | |gross weight lb= |
||
| − | |gross weight note= |
||
| − | |max takeoff weight kg= |
||
| − | |max takeoff weight lb= |
||
| − | |max takeoff weight note= |
||
| − | |fuel capacity= |
||
|more general= |
|more general= |
||
| + | |||
| − | <!-- |
||
| − | Powerplant |
||
| − | --> |
||
|eng1 number=1 |
|eng1 number=1 |
||
|eng1 name=[[Argus As 014]] |
|eng1 name=[[Argus As 014]] |
||
|eng1 type=Pulse jet |
|eng1 type=Pulse jet |
||
| − | |eng1 kn=2.7 |
+ | |eng1 kn=2.7 |
| − | |eng1 lbf=<!-- jet/rocket engines --> |
||
| − | |eng1 note= |
||
| − | |||
| − | |eng2 number= |
||
| − | |eng2 name= |
||
| − | |eng2 type= |
||
| − | |eng2 kn=<!-- jet/rocket engines --> |
||
| − | |eng2 lbf=<!-- jet/rocket engines --> |
||
|eng2 note= |
|eng2 note= |
||
| − | <!-- |
||
| − | Performance |
||
| − | --> |
||
| − | |perfhide= |
||
| − | |||
| − | |max speed kmh= |
||
| − | |max speed mph= |
||
| − | |max speed kts= |
||
| − | |max speed note= |
||
| − | |max speed mach=<!-- supersonic aircraft --> |
||
| − | |cruise speed kmh= |
||
| − | |cruise speed mph= |
||
| − | |cruise speed kts= |
||
| − | |cruise speed note= |
||
| − | |stall speed kmh= |
||
| − | |stall speed mph= |
||
| − | |stall speed kts= |
||
| − | |stall speed note= |
||
| − | |never exceed speed kmh= |
||
| − | |never exceed speed mph= |
||
| − | |never exceed speed kts= |
||
| − | |never exceed speed note= |
||
| − | |range km= |
||
| − | |range miles= |
||
| − | |range nmi= |
||
| − | |range note= |
||
| − | |combat range km= |
||
| − | |combat range miles= |
||
| − | |combat range nmi= |
||
| − | |combat range note= |
||
| − | |endurance=<!-- if range unknown --> |
||
| − | |ceiling m= |
||
| − | |ceiling ft= |
||
| − | |ceiling note= |
||
| − | |g limits=<!-- aerobatic --> |
||
| − | |roll rate=<!-- aerobatic --> |
||
| − | |glide ratio=<!-- sailplanes --> |
||
| − | |climb rate ms= |
||
| − | |climb rate ftmin= |
||
| − | |climb rate note= |
||
| − | |time to altitude= |
||
| − | |lift to drag= |
||
| − | |wing loading kg/m2= |
||
| − | |wing loading lb/sqft= |
||
| − | |wing loading note= |
||
| − | |fuel consumption kg/km= |
||
| − | |fuel consumption lb/mi= |
||
| − | |power/mass= |
||
| − | |thrust/weight= |
||
|more performance= |
|more performance= |
||
| + | |||
| − | <!-- |
||
| − | Armament |
||
| − | --> |
||
|guns= 1 X 30mm [[MK 108]] cannon |
|guns= 1 X 30mm [[MK 108]] cannon |
||
| − | |bombs= |
||
| − | |rockets= |
||
| − | |missiles= |
||
| − | |hardpoints= |
||
| − | |hardpoint capacity= |
||
| − | |hardpoint rockets= |
||
| − | |hardpoint missiles= |
||
| − | |hardpoint bombs= |
||
| − | |hardpoint other= |
||
| − | |||
| − | |avionics= |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 168: | Line 66: | ||
*[http://wp.scn.ru/en/ww2/f/2055/2/0 Blohm und Voss P.213 Picture] |
*[http://wp.scn.ru/en/ww2/f/2055/2/0 Blohm und Voss P.213 Picture] |
||
*[http://www.fantastic-plastic.com/BVP213.htm Blohm und Voss BV P.213 (1944)] |
*[http://www.fantastic-plastic.com/BVP213.htm Blohm und Voss BV P.213 (1944)] |
||
| + | |||
| − | {{Blohm & Voss aircraft}} |
||
{{Wikipedia|Blohm & Voss P.213}} |
{{Wikipedia|Blohm & Voss P.213}} |
||
Latest revision as of 20:00, 28 October 2018
| BV P.213 | |
|---|---|
| Role | "Miniature" Fighter |
| Manufacturer | Blohm & Voss |
| Primary user | Luftwaffe |
| Number built | None completed |
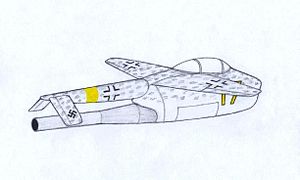
The Blohm & Voss P.213 was a prototype jet fighter powered by a pulse jet submitted by Blohm & Voss to the Miniaturjäger (Miniature Fighter) design competition of the Luftwaffe Emergency Fighter Program towards the end of the Third Reich in the Second World War.[1] The project never saw mass-production for the Miniaturjäger program was scrapped in December 1944.
History
This plane is one of the products of the latter part of 1944, when the High Command of the Luftwaffe saw that there was a dire need to put up a strong defense against the devastating allied bombing raids. Thus aircraft manufacturers Heinkel, Junkers and Blohm & Voss were asked by the Luftwaffe in November to come up with light fighter designs using a strict minimum of materials that would be fitted with one Argus As 014 pulse jet engine per unit. The resulting planes were small, spartan creations, with no radio and almost no electrical equipment, but the aim was to produce them cheaply and in large numbers so as to overwhelm the Allied bomber formations that flew daily over Germany's skies. Heinkel would use a He 162 air frame powered by a pulse jet and Junkers would submit the Ju EF 126 project.[2]
The BV P.213 is one of the first aircraft having an inverted v-tail. Unmanned drones such as the Amber, GNAT and the MQ-1 Predator would later feature this type of tail.
Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Length: 6.2 m (20 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 6 m (19 ft 8 in)
- Height: 2.28 m (7 ft 6 in)
- Wing area: 5 m2 (54 sq ft)
- Powerplant: 1 × Argus As 014 Pulse jet, 2.7 kN (610 lbf) thrust
PerformanceArmament
- Guns: 1 X 30mm MK 108 cannon
See also
References
- ↑ Mr A I Bruce. "Blohm & Voss operated Hamburger Flugzeugbau aircraft company". Wehrmacht-history.com. http://www.wehrmacht-history.com/manufacturers/blohm-and-voss-aircraft-manufacturer.htm. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ↑ "Blohm & Voss BV P.213 Luft '46 entry". Luft46.com. http://www.luft46.com/bv/bvp213.html. Retrieved 2013-06-01.
External links
The original article can be found at Blohm & Voss P.213 and the edit history here.