| Battle of Sipe-Sipe | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Bolivian War of Independence Argentine War of Independence | |||||||
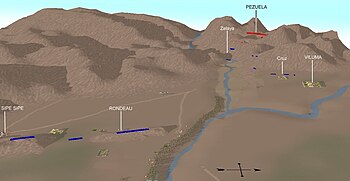 Initial situation of both armies before the battle | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
3,000 to 3,500 9 field guns |
5,100 23 field guns | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
2,000 killed, wounded or captured 9 cannons lost |
32 killed 198 wounded | ||||||
Location within Bolivia | |||||||
| |||||
The Battle of Sipe-Sipe (also known as Battle of Viluma among Spanish historians) was a major battle in the South American wars of independence in which the United Provinces of Río de la Plata (formerly the Spanish Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata) were decisively defeated by Spanish royalist forces in Upper Peru (now Bolivia). The battle took place on November 29, 1815, and resulted in the loss of Upper Peru for Buenos Aires. The area was reannexed by the Spanish Viceroyalty of Peru.
The Army of the North had been under the command of José de San Martín, but for health reasons he asked to be relieved. He was replaced by José Rondeau. At the time of the third campaign in Upper Peru (the first two had been beaten off), General Carlos María de Alvear was named by Supreme Director Ignacio Álvarez Thomas to replace Rondeau. However Rondeau's officers revolted, and communicated to him that they would obey only his orders. Rondeau, now in revolt himself, accepted the officers' proposal and remained in charge.
General Martín Miguel de Güemes, a rival of Rondeau, withdrew the support of his Gauchos and retired to Salta, taking with him the part of the army that was in Jujuy. After a successful battle in April at Puesto del Marquéz, near today's border between Bolivia and Argentina, Rondeau's army reached Potosí by June and Chayanta by September. In October, an attempt to overrun a small Royalist garrison at Venta y Media ended in defeat. Undeterred, the Army of the North occupied Cochabamba. From Cochabamba, Rondeau camped in the plateau of Sipe-Sipe, near the city of the same name. There on November 28, 1815 his forces were met by the Royalist forces from Peru under Brigadier Joaquín de la Pezuela. Rondeau had 3,000 to 3,500 men and nine field guns; Pezuela commanded 5,100 men and 23 field guns.
The result of the battle the next day was the most serious defeat of the independentist movements since the Battle of Huaqui in 1811. The insurgents' losses were estimated at 2,000 men and all of their artillery. With this defeat, the region of Upper Peru was finally lost to the United Provinces, and Spanish control was reestablished. For his success, in 1816 Pezuela was named interim viceroy of Peru by royal order dated October 15, 1815. The following year he was also promoted to lieutenant general and given the title Marquis of Viluma. Rondeau was removed from his command in 1816 and he returned to Buenos Aires.
The original article can be found at Battle of Sipe-Sipe and the edit history here.
